Rockwell Superficial Hardness Test
The Rockwell Superficial hardness test method consists of indenting the
test material with a diamond cone (N scale) or hardened steel ball
indenter. The indenter is forced into the test material under a
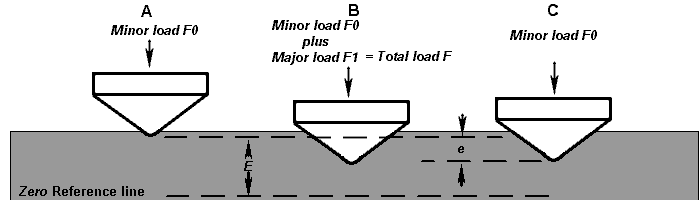
preliminary minor load F0 (Fig. 1A) usually 3 kgf. When
equilibrium has been reached, an indicating device that follows the
movements of the indenter and so responds to changes in depth of
penetration of the indenter is set to a datum position. While the
preliminary minor load is still applied an additional major load, is
applied with resulting increase in penetration (Fig. 1B). When
equilibrium has again been reach, the additional major load is removed
but the preliminary minor load is still maintained. Removal of the
additional major load allows a partial recovery, so reducing the depth
of penetration (Fig. 1C). The permanent increase in depth of
penetration, e, resulting from the application and removal of
the additional major load is used to calculate the Rockwell Superficial
hardness number.
HR = E - e
F0 = preliminary minor load in kgf
F1 = additional major load in kgf
F = total load in kgf
e = permanent increase in depth of penetration due to major load
F1, measured in units of 0.001 mm
E = a constant of 100 units for diamond and ball indenters
HR = Rockwell hardness number
D = diameter of steel ball
Larger View
Fig. 1.Rockwell Principle
Fig. 1 Rockwell Superficial Principle
Rockwell Superficial Hardness Scales
| Scale | Indenter Type | Minor Load
F0
kgf | Major Load
F1
kgf |
Total Load
F
kgf | Value of
E |
| HR 15 N | N Diamond cone | 3 | 12 | 15 | 100 |
| HR 30 N | N Diamond cone | 3 | 27 | 30 | 100 |
| HR 45 N | N Diamond cone | 3 | 42 | 45 | 100 |
| HR 15 T | 1/16" steel ball | 3 | 12 | 15 | 100 |
| HR 30 T | 1/16" steel ball | 3 | 27 | 30 | 100 |
| HR 45 T | 1/16" steel ball | 3 | 42 | 45 | 100 |
| HR 15 W | 1/8" steel ball | 3 | 12 | 15 | 100 |
| HR 30 W | 1/8" steel ball | 3 | 27 | 30 | 100 |
| HR 45 W | 1/8" steel ball | 3 | 42 | 45 | 100 |
| HR 15 X | 1/4" steel ball | 3 | 12 | 15 | 100 |
| HR 30 X | 1/4" steel ball | 3 | 27 | 30 | 100 |
| HR 45 X | 1/4" steel ball | 3 | 42 | 45 | 100 |
| HR 15 Y | 1/2" steel ball | 3 | 12 | 15 | 100 |
| HR 30 Y | 1/2" steel ball | 3 | 27 | 30 | 100 |
| HR 45 Y |
1/2" steel ball | 3 | 42 | 45 | 100 |
Rockwell superficial scales are used to test materials too thin or small for the regular scales or outside the regular ranges. Generally Diamond Indenters are used for hard materials while Ball Indenters are used on soft materials.
The HR 15 N scale is useful for testing hard thermal spray coatings like ceramics and carbides, while at the other extreme the HR 15 Y scale is used to test very soft abradable coatings.
Links To:
Hardness Testing
Rockwell Hardness Test
Rockwell Superficial Hardness Test
Brinell Hardness Test
Vickers Hardness Test
Microhardness Test
Mohs Hardness Test
Scleroscope and other hardness testing methods
Hardness Conversion Tables and Charts:
Hardness Conversion Table(colour version - may take time to load)
Hardness Conversion Table(non-colour version)
Hardness Conversion Chart (1)
Hardness Conversion Chart (2)
Chart of Brinell, Vickers and Ultimate Tensile Strength Equivalents (1)
Chart of Brinell, Vickers andUltimate Tensile Strength Equivalents (2)
Hardness Conversion Table related to Rockwell C Hardness Scale (hard materials) (colour)
Hardness Conversion Table related to Rockwell C Hardness Scale (hard materials) (non-colour)
Hardness Conversion Chart related to Rockwell C Hardness Scales (hard materials)
Estimated Hardness Equivalent Chart related to Rockwell C and Vickers (hard materials)
Hardness Conversion Table related to Rockwell B Hardness Scale (soft metals) (colour)
Hardness Conversion Table related to Rockwell B Hardness Scale (soft metals) (non-colour)
Hardness Conversion Chart related to Rockwell B Hardness Scale (soft metals)
Table of Minimum Test Piece Thickness for Rockwell Hardness Testing using Ball Indenters
Table of Minimum Test Piece Thickness for Rockwell Hardness Testing using Diamond Indenters
HV, MPa and GPa Conversion Calculator


Telephone: +44 (0)1252 405186
Email: tsc@gordonengland.co.uk
Site Links
Introducing
Nature of Thermal Spray Coatings
Surface Engineering in a Nutshell
Surface Engineering Forum
Thermal Spray Gun Repair Service
Plasma Consumable Parts
Thermal Spray Powder Supplies
Applications:
Thermal Spray Coatings on Carbon and Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymers
HVOF Coating of Paper Making Roll
Abradable Coatings
Photomicrographs
Thermal Spray Processes:
Combustion Wire Thermal Spray Process
Combustion Powder Thermal Spray Process
Arc Wire Thermal Spray Process
Plasma Thermal Spray Process
HVOF Thermal Spray Process
HVAF Thermal Spray Process
Detonation Thermal Spray Process
Plasma Flame Theory
Cold Spray Coating Process
Wear and Use of Thermal Spray Coatings
Corrosion and Use of Thermal Spray Coatings
Glossary of Thermal Spray and Surface Engineering Terms
Image Directory for Thermal Spray Coatings
Plasma Gas Flow Information
Plasma Gas Flow Correction Calculator
Contact Form
Links to other interesting sites related to thermal spray and surface engineering
Reciprocal Links
Periodic Table of the Elements
SI Units
Calculators for Conversion between Units of Measurement
Hardness Testing
Surface Engineering Message Board Archive
Surface Engineering Message Board Archive Index
Photography Gallery
Photography Gallery3
© Copyright Gordon England



