Combustion Wire Thermal Spray Process
Flame Spraying
The Combustion Wire Thermal Spray Process is basically the spraying of molten
metal* onto a surface to provide a coating. Material in wire form is
melted in a flame (oxy-acetylene flame most common) and atomised using
compressed air to form a fine spray. When the spray contacts the
prepared surface of a substrate material, the fine molten droplets
rapidly solidify forming a coating. This flame spray process carried
out correctly is called a "cold process" (relative to the substrate
material being coated) as the substrate temperature can be kept low
during processing avoiding damage, metallurgical changes and distortion
to the substrate material.
This flame spray process has been extensively used in the past and
today for machine element work and anti-corrosion coatings.
* Ceramics and cermets can be used in rod or composite wire form.
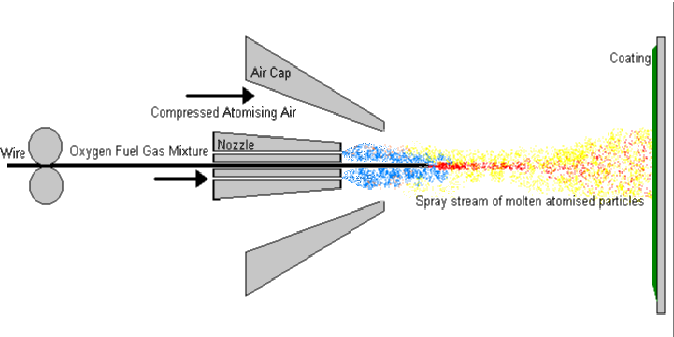
Schematic Diagram of The Combustion Wire Thermal Spray Process
(also known previously as Flame Spray, Metallizing, and Metal Spray Processes)
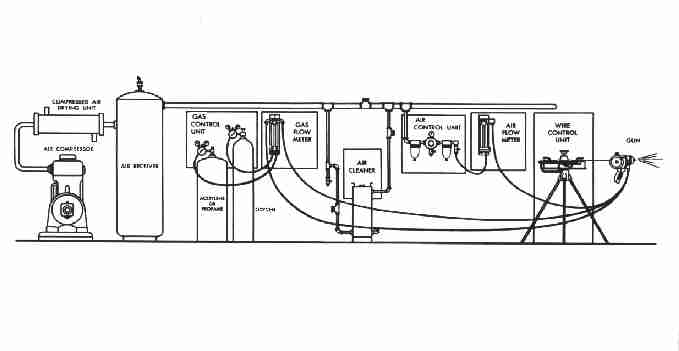
A Complete Combustion Wire Thermal Spray (Flame Spray) Process Installation
The Combustion Wire Thermal Spray Process formerly known asMetallizing, Flame Spray and Metal Spray Processes was
first invented in 1910 by Schoop in Switzerland
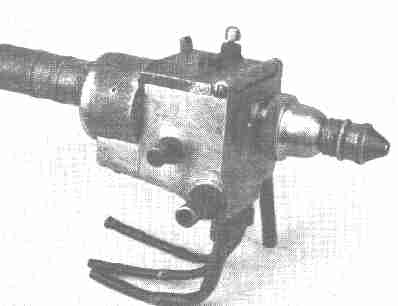
Old Type Schoop Gun
Common materials Sprayed:
- Zinc and aluminium for anti-corrosion cathodic coatings on steel
- Nickel/aluminium composite wire for bond coats and self-bonding coatings
- Molybdenum for bond coats
- Molybdenum for hard bearing applications, excellent resistance to
adhesive wear, used on piston rings, syncromesh cones and journals.
- High Chromium steel for many applications requiring hard and wear
resistant coating
- Bronzes, babbitt for bearing applications
- Stainless steels, nickel and monel for anti-corrosion and wear
- Aluminium, nickel/aluminium for heat and oxidation resistance

Recent Gun Spraying 13% Chromium Steel
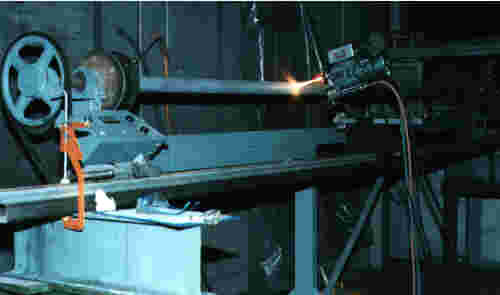
Spraying of Molybdenum Coating onto Shaft
Process Advantages:
- Low capital investment
- Simple to operate
- Wire form cheaper than powder
- Deposit efficiency very high
- Possibly still best for applying pure molybdenum coatings for
wear resistance.
- Portable system
- Preheating facility built in, unlike arc spraying
- Possible to use system in areas without electricity supply
Process Disadvantages:
- Limited to spraying materials supplied in wire or rod form
- Not capable of the low oxide, high density and high strength
coatings of plasma and HVOF


Telephone: +44 (0)1252 405186
Email: tsc@gordonengland.co.uk
Site Links
Alternative Site Recommended for Users of Netscape Navigator and Browsers Not Displaying this Page Properly







