Combustion Powder Thermal Spray Process
Flame Spray Process
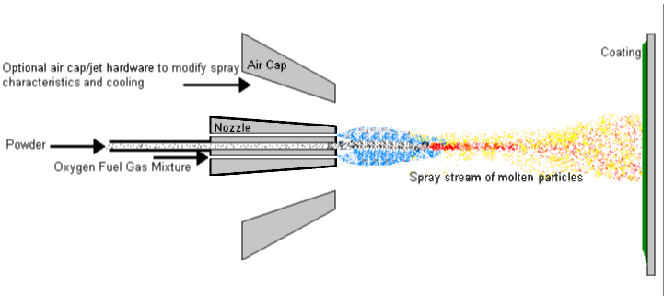

This process is basically the spraying of molten material onto a
surface to provide a coating. Material in powder form is melted in a
flame (oxy-acetylene or hydrogen most common) to form a fine spray.
When the spray contacts the prepared surface of a substrate material,
the fine molten droplets rapidly solidify forming a coating. This flame
spray process carried out correctly is called a "cold process"
(relative to the substrate material being coated) as the substrate
temperature can be kept low during processing avoiding damage,
metallurgical changes and distortion to the substrate material.
The main advantage of this flame spray process over the similar Combustion wire spray process is that a much wider range of materials can be easily processed into powder form giving a larger choice of coatings. The flame spray process is only limited by materials with higher melting temperatures than the flame can provide or if the material decomposes on heating.

